Introduction
Do you know? Nearly one-fifth of paddy would be the material of parboiled rice. More and more people have begun to realize the benefits of parboiled rice, and the market for it is becoming popular. If you want to be the manufacturer of parboiled rice, you need to buy the relative machines. I will introduce the process of how to make it, hoping helpful to you!
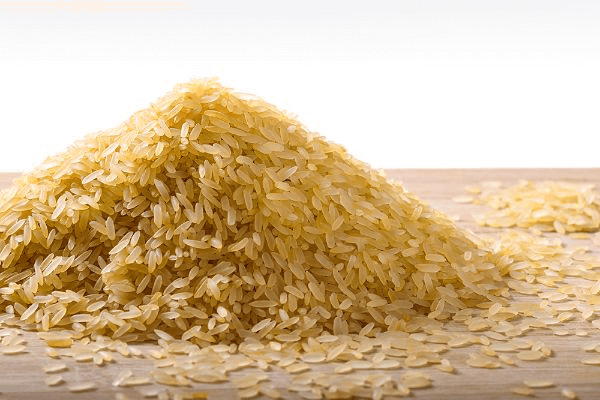
What is Parboiled Rice?
Parboiled rice, you can also call it medium well rice. The material of it is paddy and its color looks like transparent honey. During the process, there are more additional steps than the rice process, such as soaking and steaming, these steps could make the nutrients in the husk transfer to the endosperm through reverse osmosis. Parboiled rice can save the whole germ, so it can save more nutrients to a great extent and more easier to absorb for people, thus many people prefer to choose it.
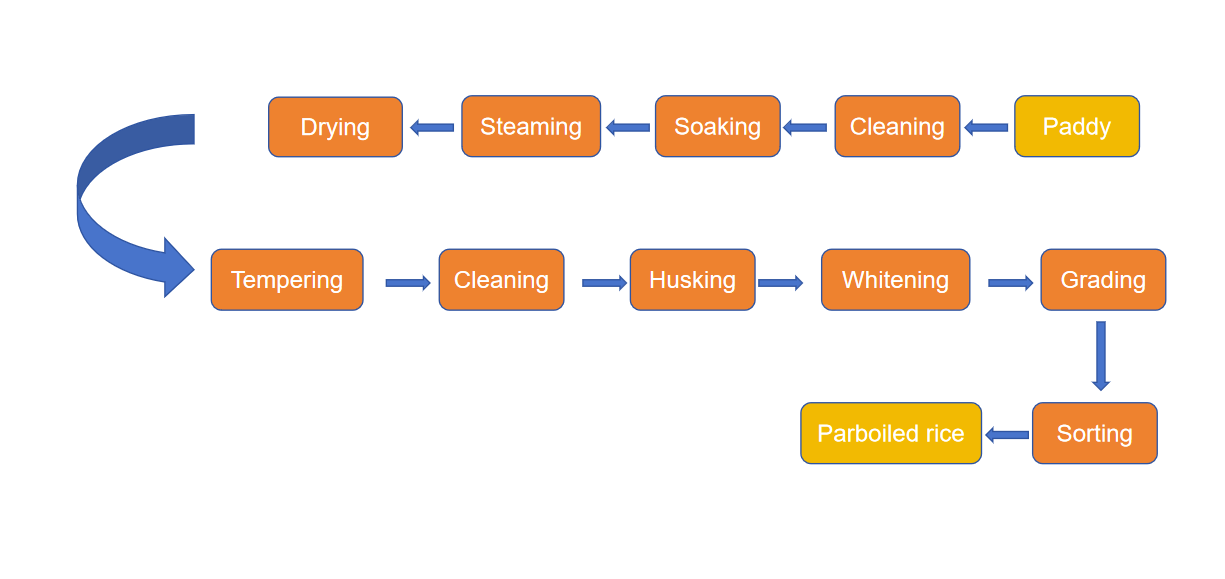
Parboiled Rice Process
As an emerging variety in the international rice trade, the parboiled rice process also progressing gradually. Compared to the traditional method, the new product line is more accurate and more convenient. The parboiled rice process is as follows:
Cleaning
Before soaking the paddy, you need to clean the paddy first. In the process of harvesting paddy, there would be some soil clumps, small stones, and broken straw, these impurities not only pollute the water, make the soaking paddy change color and taste, cause the impact of reducing the nutrients, but also cause damage to the machines in the later processing.
You need to use the cylinder’s initial cleaning sieve during the cleaning period. The cylinder cleaning screen has two layers of screens with different hole sizes. It helps remove impurities that are larger or smaller than the paddy. The air intake works with the suction system to remove dust from the paddy.
Soaking
Soaking is the first step in hydrothermal treatment, aimed at allowing paddy to absorb sufficient moisture, thereby expanding and meeting the conditions for the next step of gelatinization. When you begin to soak the paddy, it usually happens at normal pressure and can be done at room temperature or high temperature. We ANON use the high-temperature soaking method, which greatly shortens the soaking time. Instead of soaking for 2-3 days at room temperature, we only need 4-6 hours. This prevents the paddy from fermenting due to too long a soaking time, which can cause unpleasant odors.
When you operating, first heat the water in the soaking tank to 80-90 degrees. Then, place the cleaned paddy into the water to soak, keeping the water temperature at 70 degrees. Depending on the paddy variety, you may need to adjust the soaking time and temperature.
You might wonder how to tell if the paddy is soaked properly. The paddy should reach a moisture content of 40%. This ensures the paddy steams thoroughly during the steaming step; otherwise, it can become opaque, affecting the quality of your product.
Steaming
After soaking, the paddy absorbs enough moisture, so you can proceed to steam it. Steaming the paddy optimizes its starch structure, kills any insect eggs, and prevents discoloration. This process is very important for making parboiled rice, as it affects the final quality, including color and texture, which are important factors for pricing.
During steaming, it’s important to control the temperature and time carefully. This is very strict to ensure the rice is steamed properly without being overcooked. Typically, steam at 180 degrees Celsius is used at a pressure of 3-4 kg per square centimeter to steam the paddy in the steaming tank. This process, which steams the paddy, is quick and takes just a few minutes.
We ANON use high-pressure steaming in a closed container. This allows you to adjust the steam temperature freely, overcoming the limitation of regular steam, which doesn’t exceed 100 degrees. This method ensures the paddy is heated more evenly!
During gelatinization, pigments and minerals from the paddy husk and bran enter the paddy’s endosperm. Combined with browning reactions, this gives the rice a transparent honey color. You can also adjust the cooking parameters to change the rice’s color depth. At the same time, gelatinization enhances the rice’s strength and improves the whole grain rate.
Drying and Tempering
After steaming, the paddy will be drained from the tank. At this point, the paddy has high moisture and temperature from soaking and cooking, making it unsuitable for processing or storage. It needs to be dried and cooled to reduce the moisture to a safer level of 14% before processing or storage.
The paddy is transported by an elevator to the fluidized bed. In the fluidized bed, the air keeps the paddy suspended, creating a “boiling” effect. This process allows for even and quick drying, reducing the moisture content of the rice to 26%.
The paddy dried quickly in the fluidized bed and then entered a drying tower for slow, circulating drying. This process reduces the moisture content to 14% before moving on to milling and other processing steps. This helps lower the breakage rate and increases the whole grain rate.
Hot air generated by burning fuel in the boiler is blown through the paddy in the tower by a fan. This evenly removes moisture from the paddy during drying, while the exhaust air from the paddy is carried away by a suction fan.
Drying towers can be classified into batch dryers and continuous dryers based on whether the drying process is continuous. They can also be divided into cross-flow, mixed-flow, co-current, and counter-current dryers depending on the relationship between the flow direction of the grain and the hot air.
At ANON, we commonly use cross-flow drying towers because they are easy to install and have high productivity.
After slow drying, the paddy needs to enter the tempering stage. In this stage, the paddy goes into a channel without hot air, which reduces the stress formed during drying. This allows moisture from the center of the paddy to move to the surface, helping to balance the moisture distribution within the paddy.
After drying and tempering, you need to let the paddy cool down before storing it in the warehouse.

Pre-cleaning
After the initial cleaning, most impurities are removed from the paddy, making further cleaning easier. Before milling, you can choose to use equipment like vibrating screens, flat rotating screens, and stone separators for additional cleaning.
Husking
After the hydrothermal treatment, the paddy husk becomes brittle and may crack, making it easier to remove. When using a husker, you can achieve a dehusking rate of 95% to 98%. Lighter husks are blown away, leaving behind the heavier brown paddy mixture.
Paddy Separation
The brown rice mixture needs to go through a brown rice separator. This machine uses differences in weight, size, and surface friction between the rice and brown rice to separate them through the back-and-forth motion of the screen.
Whitening
During whitening, high-speed rotating rollers grind the brown rice. After hydrothermal treatment, the outer layer of the brown rice tightly bonds to the endosperm, which makes the whitening process more difficult than with regular rice. A pneumatic whitening machine cools the rice and helps remove the bran quickly, and you should set its speed to 10% faster than when processing regular rice.
Grading
The rice grader sorts parboiled rice by size, improving its appearance and helping you get a better price. The machine’s suction system also removes bran from the parboiled rice, preventing it from affecting the quality during storage.
Sorting
If you have higher quality standards for the product, you can choose a color sorter. The color sorter removes any discolored rice that has deteriorated.
Packing
Our equipment line also offers an optional packaging machine. This machine can automatically package the processed parboiled rice, saving labor and resources.

Wrap Up
I have introduced the process of making parboiled rice and the necessary machines. I believe it is a worthwhile investment. If you have plans to invest or start producing parboiled rice, feel free to contact us at ANON. We will provide you with comprehensive advice.
FAQ
What are the advantages of parboiling rice?
Besides retaining more nutrients, you can store parboiled rice longer due to its changed starch structure, and it doesn’t require strict storage conditions. It has a low glycemic index, making it suitable for diabetics and fitness enthusiasts. Additionally, steaming the rice shortens the cooking time for parboiled rice.