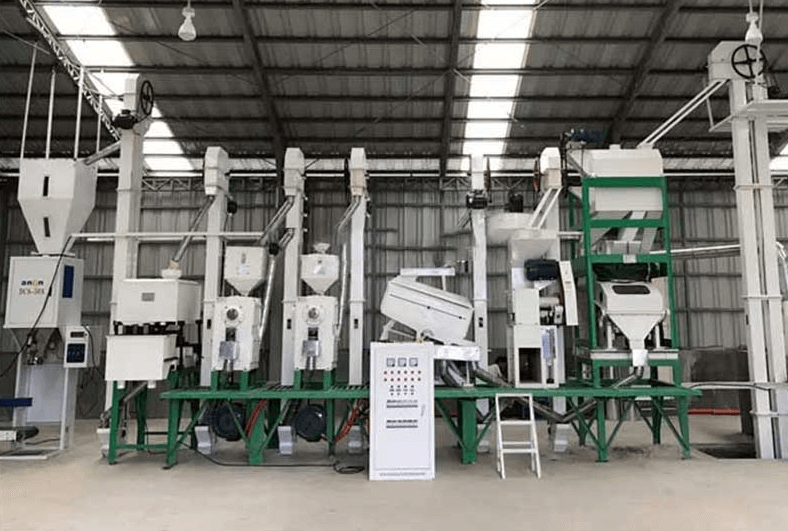
Introduction
Rice milling refers to the process of processing rice into white rice, which removes the husk of the rice and then grinds off the surface bran layer, finally obtaining the white rice we consume in our daily lives.
Rice Milling Process pdf
The rice milling process refers to a series of steps and processes for processing rice into rice. The order and relationship of each process during the processing is also very important. All steps of the rice processing flow chart will be introduced in detail below.
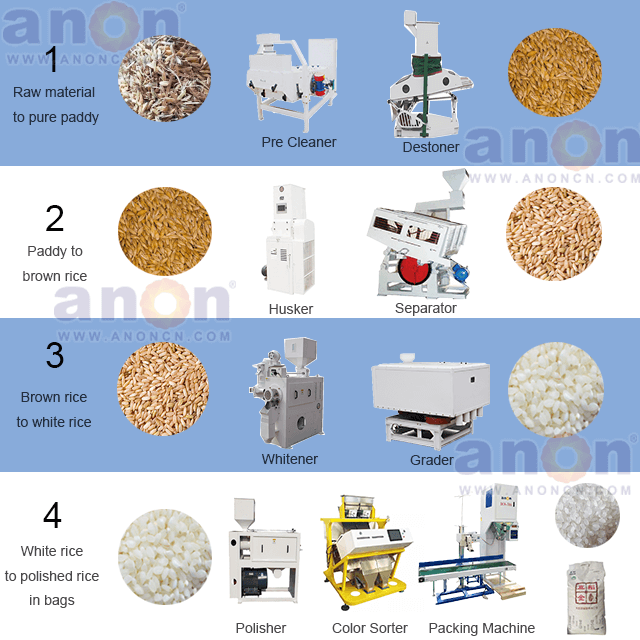
Rice Milling Process
Cleaning
The rice grains first enter the cleaning machine for cleaning. This step primarily removes hard and light impurities such as stones, straw, and dust, ensuring food safety and protecting the safety and stability of subsequent processing equipment. Machines used for cleaning include cylindrical primary cleaning screens, flat rotary screens, vibrating cleaning machines, and rice destoners. A common combination is a cylindrical primary cleaning screen and a destoner, used in both high- and low-volume production lines. Vibrating cleaning screens are generally used in production lines with a throughput of 40 TPD or higher, while flat rotary screens are used in high-volume production lines with high cleaning requirements.
Hulling
The cleaned rice grains enter the rice huller for hulling. The huller uses a pair of rubber rollers rotating at unequal speeds to squeeze and tear the rice grains, removing the husks and producing brown rice.
Paddy separation
After hulling, a mixture of rice and brown rice is obtained. The rice separator can separate the brown rice from the mixture. The rice grains then return to the huller for further hulling. The mixture is then screened again, and the brown rice is ready for the next stage of processing.
Whitening
The brown rice enters the whitening chamber of the rice whiterer, where friction and wind force remove the rice husk and germ, resulting in white rice.
White Rice Grading
After the previous processing steps, the white rice may still contain some broken grains, so screening is necessary. This is accomplished using a white rice grader. Using screens of varying apertures from top to bottom, it separates whole rice into whole rice, large broken grains, medium broken grains, and small broken grains, facilitating different processing steps and further purifying the rice’s quality.
Color Sorting (Optional)
If you’re looking for high-quality rice, you can perform color sorting. The rice color sorter machine can filter out moldy and off-color grains, further ensuring food safety and rice quality.
Polishing (Optional)
If you want to sell your rice as premium rice, a rice polisher can help. A polisher polishes the rice, refining surface cracks and creating a crystal-clear, glossy finish, enhancing the rice’s commercial value.
Packaging
The last step is to package the processed rice. You can use a rice packaging machine, which can pack the rice in a certain quantity. A fully automatic baler can also automatically complete the bagging, sewing, and transportation work. There is also a vacuum baler that can help you further facilitate storage and sales.
Rice Processing Production Line Flow Chart
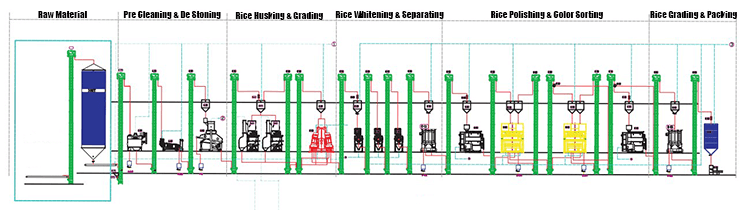
The above is a common rice process, and there may be some subtle differences in different equipment.
The rice milling process flow chart is important in the rice processing process, which may directly affect the quality and yield of rice. If you want to buy a rice mill production line, then you must know the blueprint clearly.
Conclusion
If you are interested in rice processing, we can provide complete solutions, including process design, rice milling equipment supply, and other comprehensive services. Or if you have any questions about product details, you can consult our staff. I believe that our ANON platform will provide you with satisfactory solutions.
FAQ
How much do rice farmers earn?
The average annual income for rice farmers in the United States is $28,677. Rice farmers in San Jose, California, earn the most, averaging $56,619 per year, 97% higher than the US average.
Which countries don’t eat rice?
10 countries where rice is not eaten: Ireland, Finland, Botswana, Mongolia, Lesotho, Namibia, Malta, Swaziland, Greenland, Iceland.