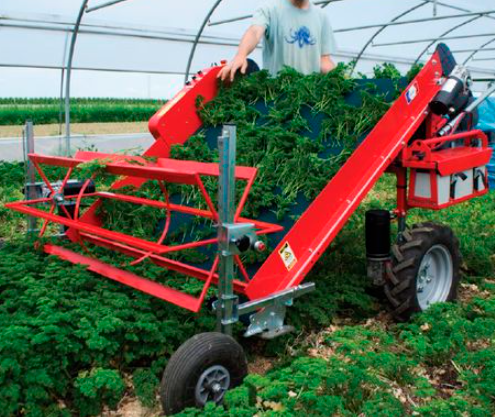
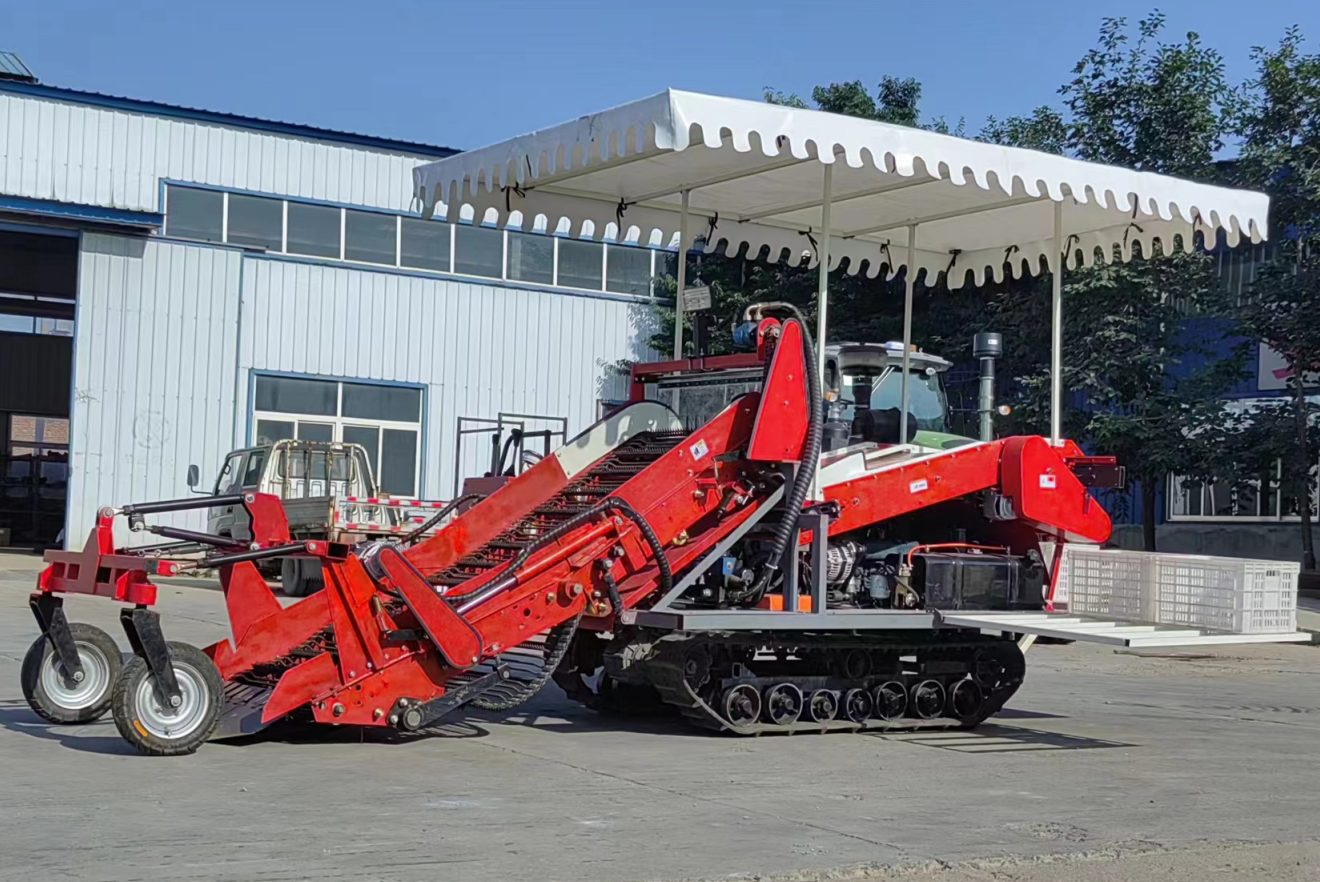
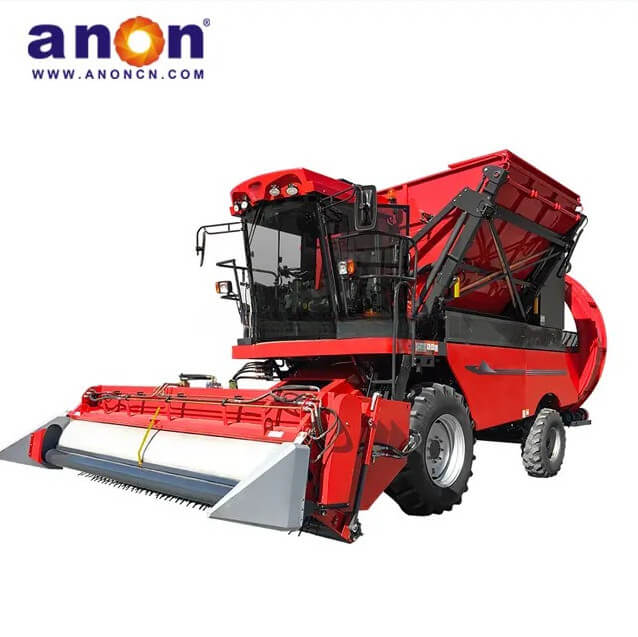
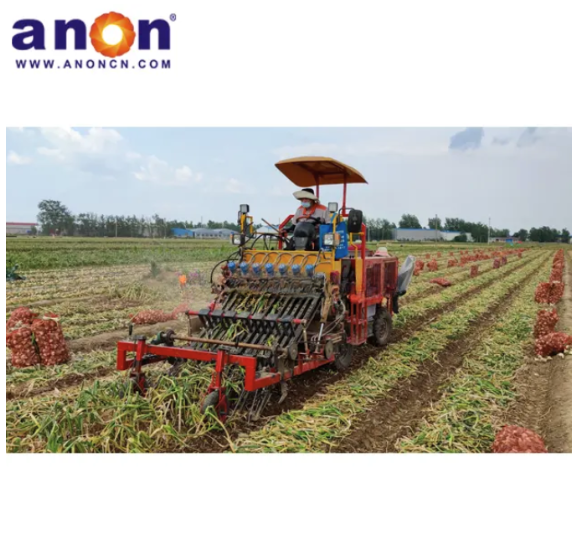
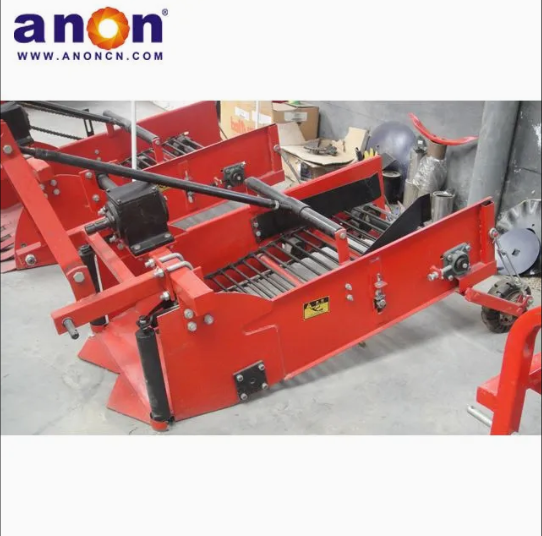
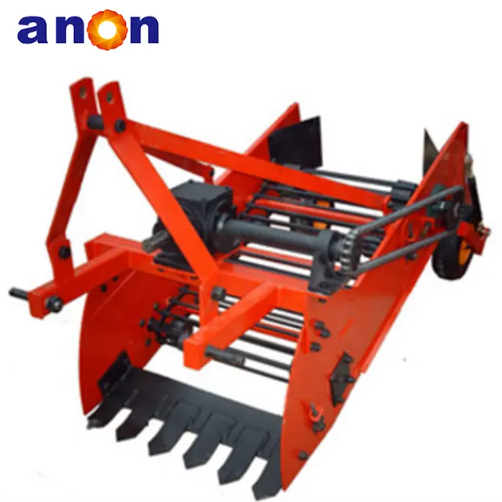
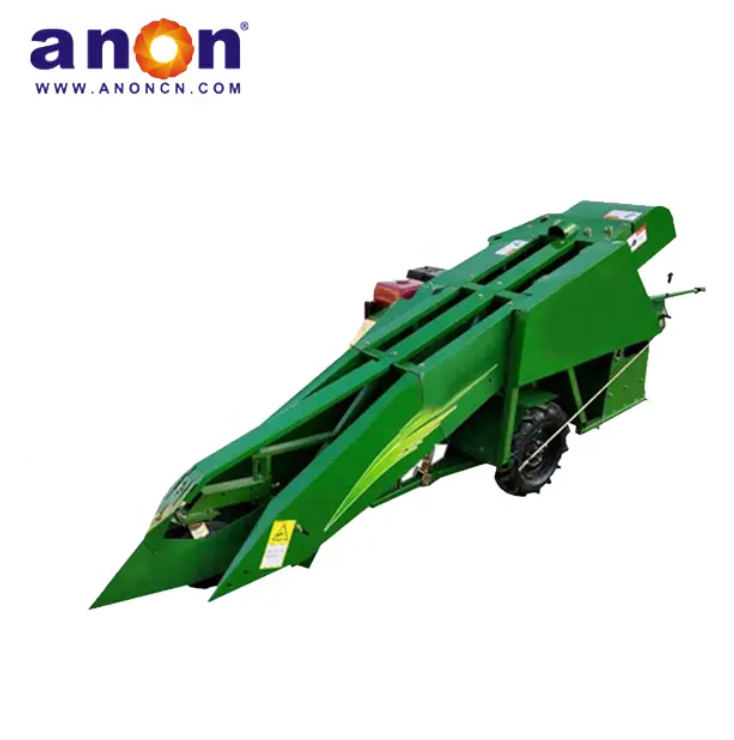
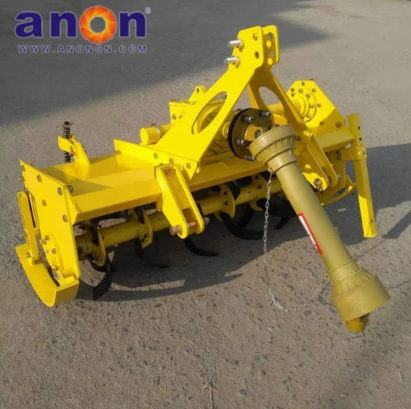
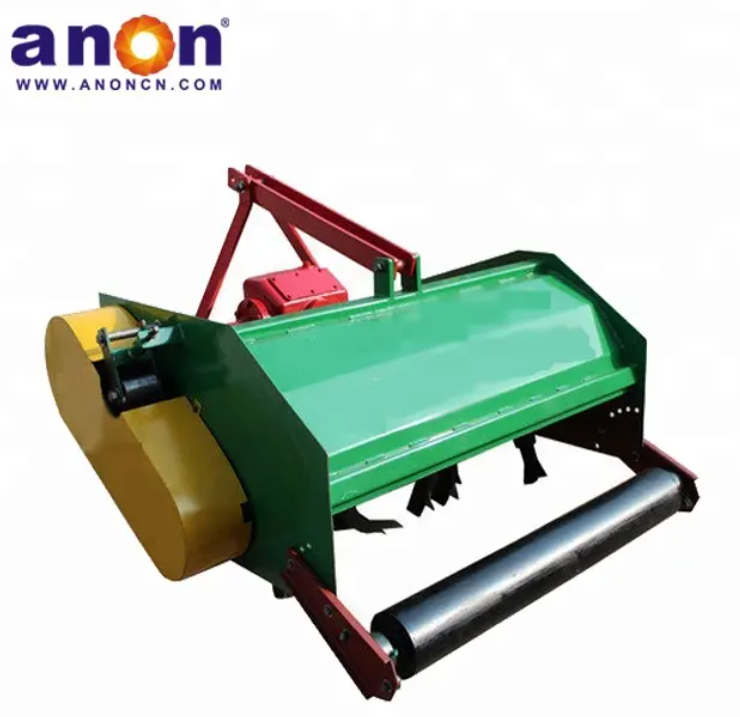
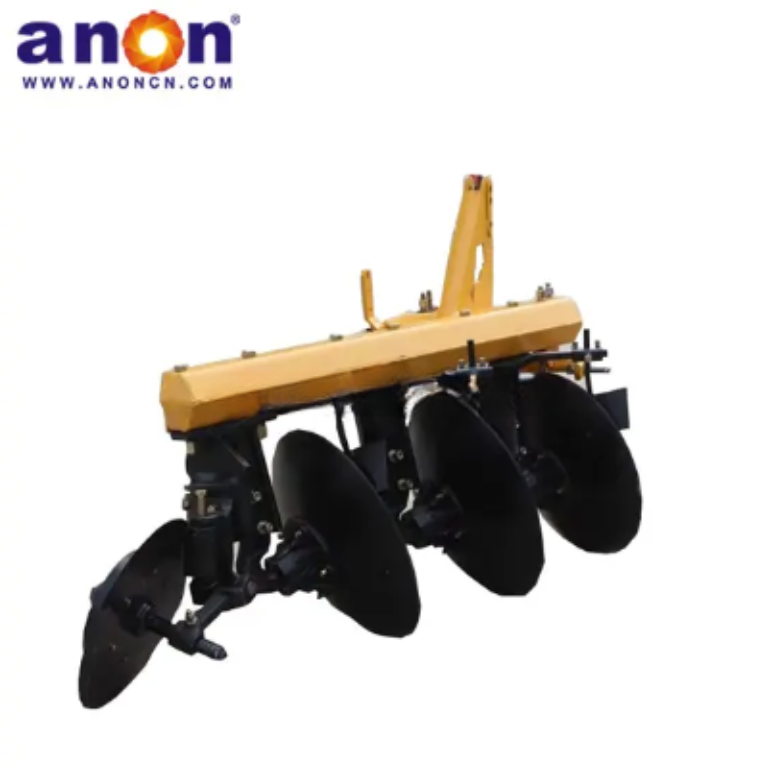
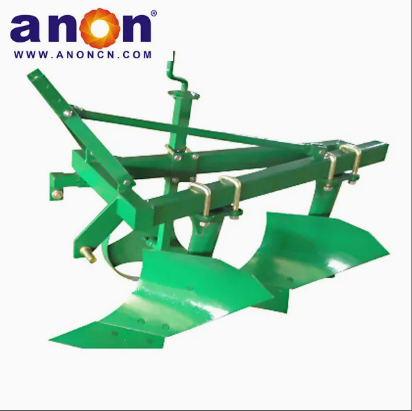
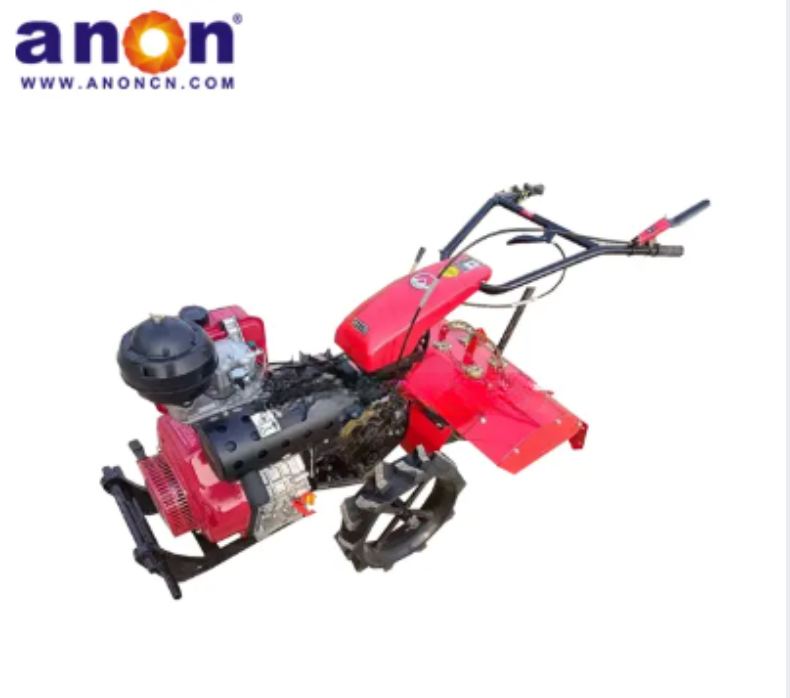
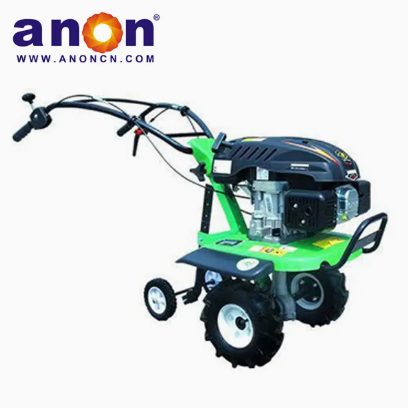
Vegetable Harvester
1. Supports in-soil, close-to-ground, and above-ground cutting to meet the harvesting needs of different types of vegetables.
2. Features a wide working width and high operating speed for improved efficiency.
3. Equipped with a contour-following mechanism that automatically adjusts the cutting height based on ground undulations.
4. Designed with user-friendly controls, making operation relatively simple.
5. Most models are powered by electric motors or lithium batteries, offering eco-friendly, emission-free performance—ideal for both greenhouse and open-field use.
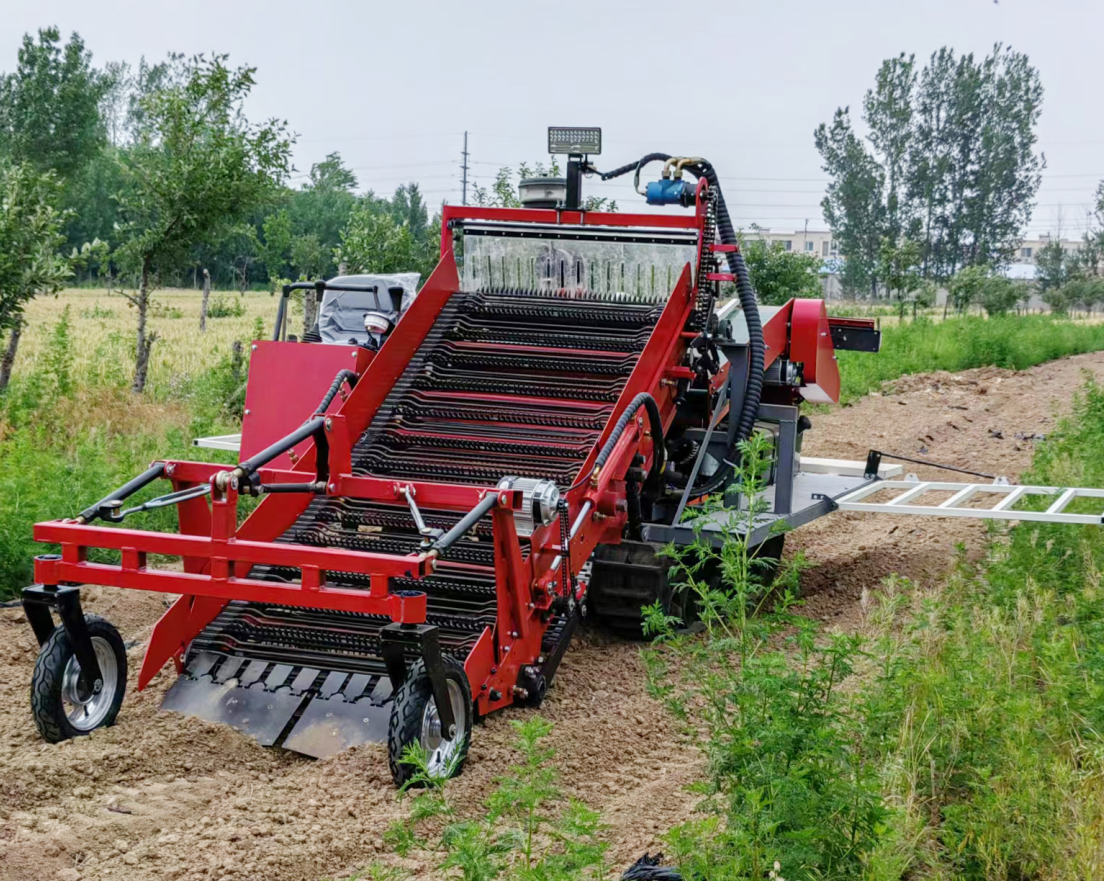

Applications
According to crop type, they can be divided into leafy vegetable harvesters, suitable for harvesting leafy vegetables such as lettuce, spinach, and celery; root and stem harvesters, suitable for harvesting root and stem vegetables such as carrots, potatoes, and onions; and fruit and vegetable harvesters, suitable for harvesting fruit and vegetable vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers.
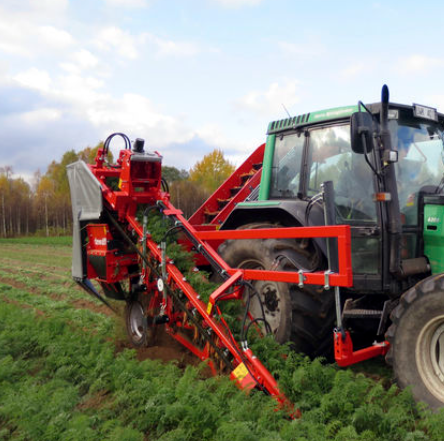

Vegetable harvesters are very suitable for various environments such as open fields, greenhouses, etc. It can efficiently complete the cutting, lifting, and transportation of vegetables such as lettuce, carrots, tomatoes, etc., making it particularly suitable for order agriculture, fresh food distribution bases, organic plantations, and labor scarce areas. By improving harvesting efficiency and crop integrity, it meets the needs of modern agriculture for precision and high-quality operations.
Operate Tips
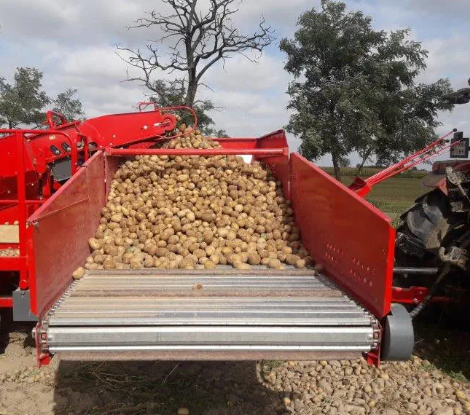


FAQ
Radishes are probably the fastest-growing vegetable in your garden, and can be harvested in as little as 30 days after sowing. Cabbage can be harvested in as little as 50 days after sowing, and this vegetable also prefers the cooler spring and fall weather.
Ginger is one of the most profitable crops due to its versatility and high demand. Choosing young ginger can be harvested faster and fetch a higher price in the market, making it a wise choice for farmers looking to increase their profits.
First, clarify the type of vegetables. For leafy vegetables, choose cutting type; for root vegetables, choose digging type; for fruit and vegetables, give priority to semi-automatic models;
Second, clarify the planting scale: choose small machines for small areas; for large-scale planting, consider large and efficient models.
Third, consider the terrain and environment: choose electric crawler type for greenhouses, and wheeled or diesel-powered models for open fields.
Finally, consider after-sales and accessories: choose brand manufacturers to ensure convenient parts supply and maintenance services.