Introduction
The moldboard plow is an essential tool in agriculture, and its performance directly affects the quality of farming. As agricultural technology advances, the design of the moldboard plow has been improving as well. Understanding the plow better will help you choose the right tool for your needs. In this article, I will share some useful information about moldboard plows. Keep reading if you’re interested!
What is a Moldboard Plow
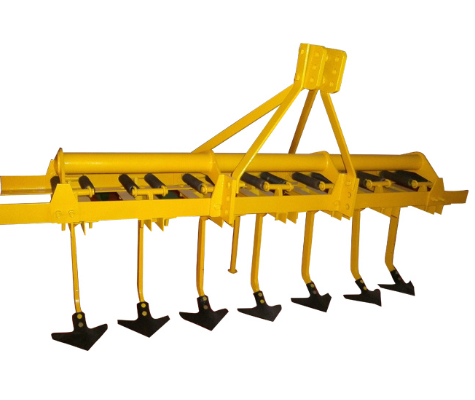
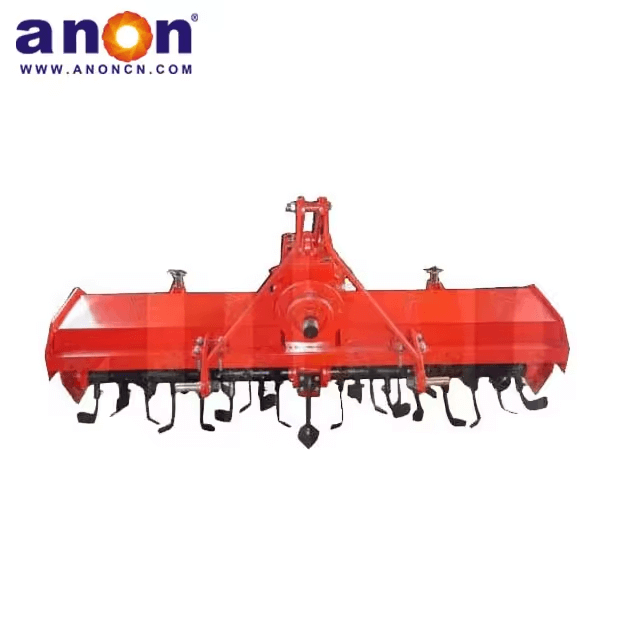
The moldboard plow is a widely used land preparation machine in the agricultural field, with the plowshare and plow wall as the main working components. Using the moldboard plow to plow land can bury residual weeds and fertilizers on the surface of the field into the soil layer. After plowing, the soil is fragmented and loose, creating suitable conditions for sowing and crop growth. It is the most widely used and numerous type of tillage equipment among various farming tools.

How a Moldboard Plow Works?
Moldboard Plow Parts and Function
Working Parts of the Moldboard Plow
Plowshare: Also called a plough blade. When you drive the machine forward, the ploughshare cuts into the soil. Its sharp front edge helps it enter the ground easily. The back part gets wider to turn over and break up the soil.
Moldboard: Connected to the ploughshare and located just above and behind it, the moldboard helps form the curved surface that turns the soil. It breaks up and flips the soil lifted by the ploughshare, making the soil loose and well-aerated.
Plowside Plate: Also known as the plow bed, it is installed on the left side of the plow frame. It supports and balances the side pressure generated during plowing, ensuring the plow operates stably.
Plow Beam and Plow Column: The plow holder is used to connect various components, including plowshare, plow wall, plow side plate, and plow column, all of which are installed on the plow holder; And the plow column connects the plow body and the frame, and transmits the traction power to the plowshare, driving the plow body to cut into the soil.
Small Front Plow: Located on the left front side of the main plow body, it cuts and flips the topsoil, crop residue, and weeds into the newly plowed furrow. This helps improve the quality of the plowing job.
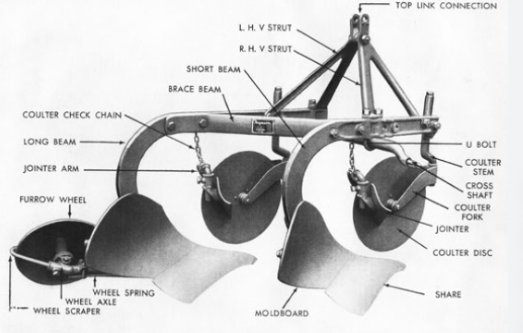
Hitching Device: The hitching device connects the moldboard plough to the tractor. Common types include the three-point hitch and the two-point hitch.
Depth Wheel: The depth wheel adjusts the working depth of the plough. It prevents the moldboard plough from cutting too deep or too shallow, ensuring smooth and stable operation.
Adjustment Mechanism: The adjustment mechanism is used to set the plough’s working depth, angle, and lateral position to meet different farming needs. It usually includes a hydraulic system or mechanical screw, offering easy operation and high precision.
Coulter: Positioned in front of the main plough body, the coulter cuts vertically through soil, weeds, and crop residues during operation. It helps create a clean furrow wall, reduces resistance on the main plough body, improves tillage quality, and prevents the furrow wall from collapsing, making future ploughing easier.
Press Wheel: The press wheel compacts the soil after tillage. It reduces moisture evaporation and improves the soil’s ability to retain water.
Covering Board: Mounted behind the plough body, the covering board helps level the turned soil or cover seeds with soil after planting.
The Working Principle of the Moldboard Plow
When the tractor works with the moldboard plow, the plow body cuts into the soil under its own weight, and the power is transmitted from the tractor. The plowshare and moldboard create a curved surface that first enters and cuts the soil. Then, the soil clods are broken and flipped along the moldboard, covering the surface weeds into the newly plowed furrow, mixing the topsoil with the deeper soil layers.
Types of Moldboard Plows
Connection Method
The moldboard plow needs to be used with a tractor to complete its work. Based on how the plow is connected to the tractor, Bottom plows can be divided into three types: the trailing plow, the mounted plow, and the semi-mounted plow.
Traction type
The trailing moldboard plow is connected to the tractor by a single point. Its structure is simple, and the tractor pulls the plow during operation. When not in use, the weight of the plow is fully supported by the plow wheels.
Suspending Type
The mounted moldboard plow is connected to the tractor’s three-point hydraulic hitch. This allows you to raise and lower the plow and adjust the working depth. When transporting, the weight of the plow is supported by the tractor.
Half-suspending Type
The half-suspending moldboard plow combines features of both the trailing and mounted types. The front part of the plow is connected to the tractor’s hydraulic system through a suspension frame, but it is not fixed. Instead, it is connected by linkages. When the hydraulic system lifts the plow, only the front end is raised. This provides good stability while still being flexible. During transport, the weight of the plow frame is shared by the plow wheels and the tractor.
Shape
Based on shape, mouldboard plows can be divided into two types: the mirror plow and the bar plow.
Mirror Plow
The moldboard of the mirror plow is a smooth, continuous curved surface. It appeared earlier, and its manufacturing process is well-established. It’s easy to make, doesn’t easily pick up film or straw, and doesn’t cause clogging. When flipping the soil, it buries weeds and straw deeper into the soil.
Bar Plow

The moldboard of the bar plow has a bar-like structure, which reduces the contact area between the moldboard and the soil, helping to minimize soil sticking. The bar design also helps break up the soil more effectively, improving soil crushing. The bar structure is also easier to replace.
Function
Dryland plow
A dryland plow is suitable for dryland cultivation, with a small plow body and strong soil-breaking ability.
Water field plow
The water field plow is designed for paddy fields, with a wide plow body and strong anti-sinking performance. It has the function of breaking and suspending the plow.
Orchard plow
The orchard plow is suitable for vineyards or other orchards, with a small size and flexible operation. It can be used as a high ridge to cover grape stems or has a plow body that can automatically expand and contract horizontally, which can plow the soil near the fruit tree trunk, and is suitable for inter-row cultivation of fruit trees.
Bidirectional flipping plow

During the back-and-forth travel of the plowing operation, the bidirectional flipping plow can alternately flip the plow to the right or left, making the plow always tilt in the same direction, reducing empty rows on the farmland and improving efficiency. It is most suitable for cultivating sloping land, and multiple plows can gradually reduce the slope. It is divided into full flip type (two sets of plow bodies arranged 180 ° relative to each other) and semi flip type (two sets of plow bodies with an angle greater than 90 ° and a turning angle less than 90 ° when reversing).
Amplitude modulation plow
The amplitude modulation plow is a type of plow with an adjustable working width. Its design adjusts the lateral spacing of the plow body by changing the angle α between the main inclined beam and the forward direction, thereby adapting to different operating conditions and improving operating efficiency.
Deep plowing
The depth of cultivated land with deep plowing exceeds that of ordinary plows, generally reaching 30-45 centimeters. It is suitable for deep loosening of soil and improving soil structure.
Land plow
A land plow is used for cultivating shrubs and wastelands, with a large and bulky body. Ploughshares are usually made in a straight pole shape to prevent breakage and have efficient soil-breaking ability.
Number of plows
Single plow

A single plow is equipped with only one plow body, with a simple structure, suitable for small-scale cultivation or complex terrain areas. It is suitable for mountainous areas, hilly regions, or small-scale farmers for personal use.
Double plow

The double moldboard plow is equipped with two plow bodies, which can plow two ridges and grooves at once. Its efficiency is higher than that of a single plow, but it still requires less power traction. Suitable for small and medium-sized farms.
Multiple plows
Multiple plows are equipped with three or more plow bodies, and common models include three plows, four plows, six plows, etc. They require high-power tractor traction and are suitable for large-scale cultivation.
Advantages of Moldboard Plow
First, the moldboard plows effectively control weeds. Their plowshares easily cut through the soil surface, penetrating deep into the earth and burying weed seeds during tilling, significantly reducing germination rates and decreasing the need for chemical herbicides.
Second, the tilling process with a moldboard plow mixes crop residues, organic matter, and fertilizers with the soil, improving soil structure and fertility, while also enhancing soil aeration and water permeability.
Furthermore, plowing with a moldboard plow is convenient; simply inserting the plow blade into the soil is all it takes to till, making it simple and labor-saving. Moldboard plows can also adapt to the needs of different crops, adjusting the plowing depth and spacing according to the specific characteristics of each crop. The loosened soil after tilling provides an excellent environment for seed germination and early seedling growth.
Disadvantages of Moldboard Plow
The moldboard plow mainly relies on the front part of the plow point to do the work. This means that if it encounters hard objects, the front of the plow point can be easily damaged, causing the entire plow to stop working properly.
In addition, the moldboard plow uses more power than other types of plows. This is because its structure is more complex, and it requires more energy to overcome the soil’s resistance and friction.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Moldboard Plow
Plowing Depth
The root length of each crop varies, so it’s important to plow the soil based on the crop’s needs. Plowing depth is key when choosing a Bottom plow. You should check if the plow can reach the required depth for the crop’s growth. Also, make sure the plowing depth is consistent. Except for differences in soil type and moisture, the Bottom plow depth should be stable and more than 90% accurate.
Soil Crushing Rate
The moldboard plow needs to break the soil into a state suitable for planting and sowing, so the soil crushing rate is very important. For agricultural needs, the crushing rate of the Bottom plow should be over 80%. Therefore, when choosing a plow, be sure to pay attention to its soil-crushing rate.
Tractor
Moldboard plows with different connection types have different requirements for tractors. If you have already purchased a tractor, you need to make sure that the plow you choose can be properly connected to your tractor.
In addition to the connection type, you also need to consider the moldboard plow’s maximum plowing depth, working width, number of bodies, tractor’s pulling power, plowing resistance, and traction coefficient. These are represented by the letters a, b, n, P, K, and η, respectively.
The formula for calculation is::n=(P×η)/(K×a×b)
The plowing resistance coefficient (η) is generally between 0.8 and 0.95.
This way, you can calculate whether to buy a single-share, double-share, or multi-share plow based on your existing tractor. Alternatively, you can choose the right tractor depending on the mouldboard plow you plan to buy.
How to use a moldboard plow
To get the most out of your mouldboard plow, you must know how to use it correctly. Next, I will explain some useful tips for using the plow.
Land Preparation
Before using the mouldboard plow for tilling, you need to prepare the land. This includes clearing debris, especially hard rocks, to avoid damaging the plow point. Doing this can also help increase the tilling speed. For drier soil, you can moisten it, and for soil with too much moisture, let it dry out a bit.
Adjusting Plowing Depth
As I mentioned earlier, plowing depth should be adjusted based on the crop’s needs. So, each time you plow, make sure the moldboard plow’s depth meets the requirements for the crop you’re planting. You can adjust the depth by changing the height and position of the plow.
Height Adjustment refers to adjusting the height of the depth control wheel. The suspension system can only adjust the plow’s lift, so if you need to increase the plowing depth, raise the depth control wheel. To decrease the depth, lower the wheel.
Position Adjustment involves moving the adjustment handle. By controlling the relative position between the tractor and the plow, you can adjust the plowing depth. This helps the moldboard plow maintain a consistent depth even on uneven ground.
Conclusion
I hope that after reading this article, you will have a better understanding of the moldboard plow. Since our founding, ANON has been dedicated to exporting agricultural machinery. We offer a variety of mouldboard plows and are happy to help with any questions or purchasing needs you may have. Feel free to contact us!
FAQ
1. Is the mould board plough primary or secondary?
The moldboard plow is used for primary soil tilling. Its plow point effectively breaks the surface soil, flips it over, and mixes it. The typical plowing depth is between 20 to 25 cm.
2. What is the difference between a disc plough and a Mouldboard plough?
The moldboard plow and the disc plow have different working parts. The moldboard plow uses the plow point to slide and turn the soil, while the disc plow uses rotating discs to till the land.
3. What horsepower does a moldboard plow have?
Working widths: 14 inches (single-bottom) and 28 inches (double-bottom) to meet different tillage needs. Horsepower range: Suitable for tractors from 20 to 50 horsepower, providing flexibility for small to medium-sized tractors. Efficient soil preparation: A 14-inch cutting width allows for precise soil turning and aeration, resulting in optimal planting conditions.













