Introduction
In agricultural work, land preparation is a very important step at the beginning of all cultivation. There are generally two methods of land preparation: tilling and plowing. So many friends have asked which one should be chosen: tiller or plow? This article will explain the differences between the two from the aspects of working principle, land leveling effect, operation, maintenance, etc.
Working principle
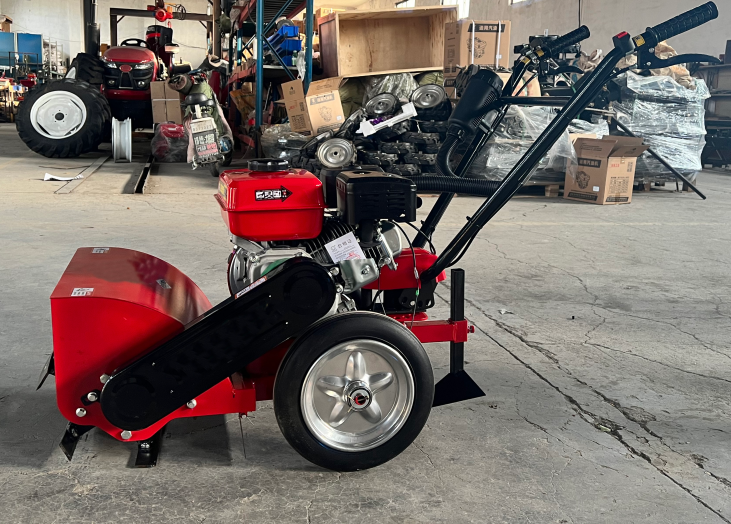
The tiller or rotary tiller mainly relies on the power of the engine or tractor to drive the blade shaft to rotate at high speed through the transmission system. The L-shaped or curved blade on the knife roller cuts into the soil like a “rotating claw”, shredding, throwing, and evenly scattering the soil blocks backwards. While operating, turning soil blocks, straw, weeds, etc. into the soil to make it soft and fine, preparing for sowing or planting crops, is like giving the land a ‘deep massage’.
A sharp plow blade cuts into the soil, and under the traction of the tractor, it flips up the bottom of the soil layer and pushes it laterally to achieve deep plowing. As the main tool used in modern agriculture for plowing, it can mechanically help you break soil compaction and bury weeds or residues. This can help you improve soil permeability and quality, creating favorable conditions for crop growth.
Types
Tiller
There are various types of rotary tillers. According to the installation method of the blade shaft, there are horizontal axis, vertical axis, and inclined axis.
Horizontal axis rotary tiller
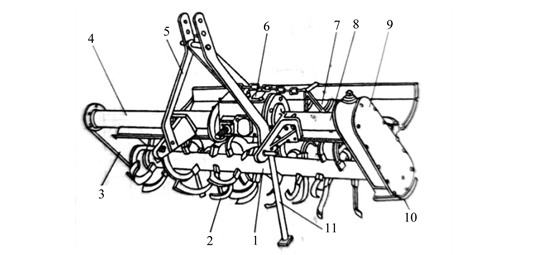
The horizontal rotary tiller arranges its blade shaft horizontally, and the blades evenly distribute themselves in a multi-head spiral pattern on the blade shaft. The tractor’s power drives the blade shaft to rotate through the transmission device, and the blades chop and scatter the soil like sawing wood. Subsequently, the soil blocks were thrown back and up, collided with the casing and trailer, further shattered, and finally spread flat on the surface. The horizontal rotary tiller has strong soil-crushing ability and good soil-preparation effect, suitable for direct sowing and transplanting. However, it consumes more fuel and has high resistance to the rotation of the blade shaft, making it unsuitable for clay.
Vertical shaft rotary tiller

The blade shaft of the vertical rotary tiller is arranged vertically, with several rows of curved blades installed below, which rotate around the vertical shaft. When working, the blade shaft rotates rapidly, and the blade drills down from the soil surface like a “drill bit”, breaking up and turning the soil blocks while throwing the soil out in all directions. After colliding with the machine casing, it becomes finer and finer. Due to the vertical axis of the blade, the blade mainly moves in the vertical direction, causing the soil to be flipped vertically. The vertical rotary tiller is particularly suitable for paddy field operations, such as plowing rice fields. It can fully mix rice stubble and soil and has a good effect on breaking up soil and making slurry. However, the soil thrown out by the vertical rotary tiller is not very uniform, and the coverage is slightly poor.
Inclined rotary tiller
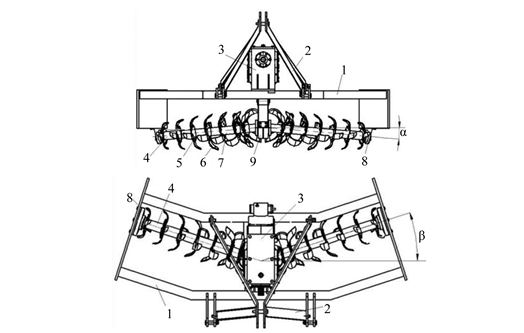
The blade shaft of a tilted rotary tiller is usually inclined at a 45-degree angle to the ground, and the blades form a “spiral upward” trajectory when rotating. It is like a tilted drill bit, capable of turning deep soil to the surface while pressing surface soil into deeper layers. The tilted blade generates a lateral force when rotating, throwing the soil block to both sides, covering a wider range and suitable for returning straw to the field or mixing soil. It breaks the soil more evenly and has better coverage, making it especially suitable for dryland operations. It can fully mix straw and soil blocks and also loosen the soil for ventilation.
Plow
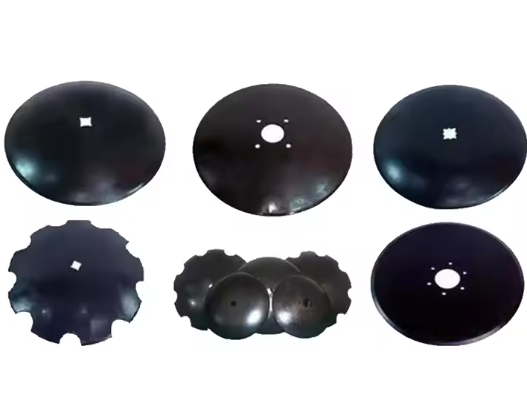
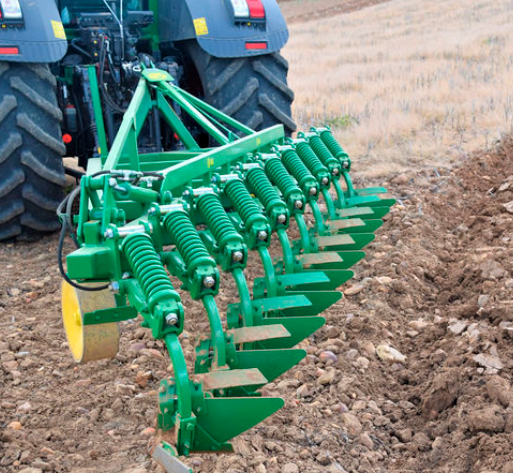
Disc plow

The disc plow uses a concave disc as its working component, and the sharp edge of the disc can cut into the soil under the rotation of the disc. Then, the soil shaft rises along the concave surface of the disc, and with the help of a scraper plate, the soil is flipped and crushed. The disc plow is suitable for heavy, dry, and hard soils with multiple stones and roots, especially for green and fertile fields, grass roots, and areas with many stones, as well as heavy and sticky soils. Because the disc plow cuts through the soil with the continuous rotation of the disc, it can cut through weeds and crop roots, making it less prone to entanglement and blockage.
Moldboard plow
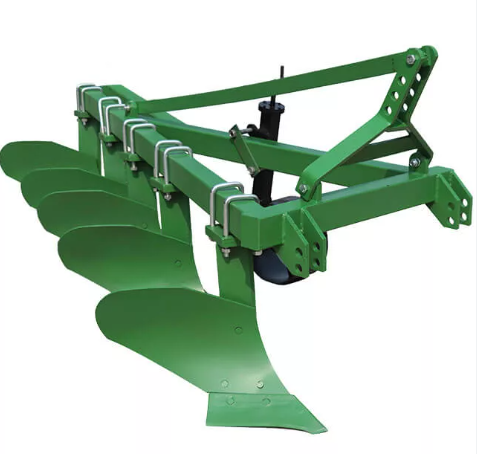

The moldboard plow uses a triangular plowshare to cut into the soil, and under the traction of the tractor, the bottom of the soil layer is lifted up. Then, the curved plow wall flips the soil block completely like a flipping board and pushes it to one side while burying weeds and debris. This method is equivalent to turning over the land, which can help you break through the hard soil layer, improve the soil structure, and achieve soil fragmentation and turning.
Land preparation effect
Tiller: Firstly, the rotary tiller has high work efficiency. It takes about 20 minutes to rotate one acre of land twice, which greatly shortens the time and saves labor compared to plowing. Secondly, the soil after rotary tillage is relatively fine, and there will be no large soil lumps in the field. Moreover, it can adapt to different soil types and has a wide range of applications. However, the tillage layer of rotary tillage is relatively shallow, usually 12 to 15 centimeters, which is suitable for shallow soil loosening and crushing operations.

Plow: The plowing layer is relatively deep; for example, small plowing machines can reach a plowing layer of 20-25 centimeters, while some large plowing machines can reach a plowing layer of about 30-35 centimeters, which has a good effect on improving the soil. Deep plowing accelerates straw decay, thoroughly tills the soil layer up and down, and reduces pest and disease occurrence, especially in fields with returned straw.Plowing takes a longer time compared to rotary tillage, and after plowing, it also requires raking, which is more time-consuming and labor-intensive.

Crop type
The different tillage depths of rotary tillers and plows also determine the different crops to be sown for consumption. So, choosing a machine based on the crops you want to plant will be clearer.
A rotary tiller is suitable for crops such as cotton and peanuts that require frequent loosening of soil, as well as vegetables that do not require deep plowing. And deep cultivation
Grain crops such as wheat, corn, sugarcane, etc., require plows to create sowing depth.
Fuel consumption
Because rotary tillers are mainly used for shallow cultivation of land, with a cultivation depth generally not exceeding 20 centimeters, shallow operation resistance is relatively low, and under the same cultivation area, it will save more fuel.
The plow relies on the plowshare to move the soil, which requires overcoming greater resistance, especially during deep plowing when the resistance significantly increases. Deep plowing usually costs 25 to 30 centimeters and requires more power. If encountering hard soil layers or areas with many stones, fuel consumption will further increase.
Application
Tiller: A rotary tiller is suitable for shallow tillage of loose, sandy, or medium-viscosity soil, especially when the soil moisture content is moderate. Before sowing, it can help you quickly break up soil blocks and mix straw for returning to the field, creating good conditions for sowing. Or it can be used for rice field tillage, which can quickly plow rice stubble, reduce pests and diseases, or for protective tillage, rotary tiller combined with straw covering technology can reduce soil erosion.
Plow: Plows are suitable for various soil types, especially in heavy or hard soil layers, and have significant effects. P can achieve a plowing depth of 20-25 centimeters, used to break through the plow bottom layer. It has a slower operating efficiency compared to rotary tillers, but its plowing depth effect is more thorough. It is suitable for deep plowing in dry land and can improve soil permeability and water retention by breaking the plow bottom layer, promoting root development. The improvement of saline alkali land can be achieved by deep plowing to press salt into the deep layers, reducing surface salinization. It is also suitable for newly cultivated land, plowing the soil layer, and accelerating soil maturation.
Which is better for soil?

Soil structure
Firstly, in terms of soil structure, plowing can improve soil structure by reducing soil compaction in deep layers and enhancing the soil’s ability to retain water and nutrients. The rotary tiller can quickly chop up the soil in shallow tillage, reducing the evaporation of surface soil moisture. However, long-term use of rotary tiller can cause the tillage layer to become shallower, the plow bottom layer to thicken, and hinder the circulation of soil moisture, nutrients, and air.
Soil quality
Plow can deeply bury straw, insect eggs, and pathogens through deep plowing, reducing the occurrence of pests and diseases. Deep plowing increases gaps between soil particles, improving permeability and airflow, which benefits root growth. Shallow burial depth of rotary tiller straw may increase the occurrence of pests and diseases.
In general, plowing is more suitable for improving deep soil structure, reducing pests and diseases, or enhancing soil water retention capacity. If rapid soil fragmentation, reduction of topsoil evaporation, or shallow soil preparation are required, rotary tillers are more efficient.
Maintenance
Cleaning and inspection after homework
After using the rotary tiller, you need to clean the straw and soil on the rotary tiller blade and blade shaft in a timely manner to prevent entanglement and blockage. Check the wear of the rotary tiller blade and replace it promptly if the blade becomes dull or has a notch.
After plowing, immediately use a high-pressure water gun or brush to remove soil from the plow body, plowshare, and plow wall to prevent corrosion. Check the wear of the plowshare, plow wall, and plow column, and replace them promptly if the wear exceeds 10%. Apply lubricating grease to the bearings, pins, and connecting parts of the plow to reduce friction and rust.
Regular maintenance and adjustment
For rotary tillers, you need to regularly replace the lubricating oil in the gearbox to ensure lubrication effectiveness and avoid machine stalling during operation. During homework, adjust the blade shaft speed according to soil conditions. When the soil is hard, reduce the speed, and when the soil is soft, increase it appropriately.
For plows, in daily work, you need to adjust the plowing depth according to soil conditions to ensure consistent plowing depth and avoid excessive wear and tear. For some special machines such as hydraulic flip plows, you need to regularly check the hydraulic system, check the hydraulic oil level and quality, and replace the hydraulic oil. Check and tighten all bolts and connectors to prevent loosening and potential malfunctions.
Long-term storage
Before long-term storage, it is necessary to spray rust-proof paint or oil on the surface of the metal parts of the rotary tiller and plow to avoid oxidation. And try to store them in a dry and ventilated place to avoid rusting and corrosion caused by humid environments.
Buying Tips
According to your needs
If deep plowing, improving soil permeability, or reducing pests and diseases are needed, it is recommended to choose a plow. If you need to quickly level the land, improve the flatness, or if the plot is small and requires frequent operation, a rotary tiller is more suitable.
Consider your land condition
If the land you want to cultivate is sticky or has a high moisture content, the plow may be difficult to operate due to the high soil viscosity, and the rotary tiller is more flexible. If you want to cultivate straw returning land, plowing can accelerate straw decay faster and reduce pests and diseases.
Budget
The price of rotary tillers is relatively low, with high operational efficiency and suitable for short-term investment. The price may be slightly higher, but deep plowing has good effects and can help improve soil quality and crop yield in the long run.
If conditions permit, plows and rotary tillers can be used alternately to achieve both deep plowing and leveling effects.
Conclusion
Through the above explanation, I believe you have gained a certain understanding of rotary tillers and plows and have a deeper understanding of the effects of rotary tillage and plowing. ANON Agricultural Machinery has been deeply involved in the industry for over 20 years, committed to providing professional machines and satisfactory services to global customers. If you have any needs, feel free to contact us at any time!
FAQ
When should I plow the land?
Spring plowing is mainly for prevention. Plowing is usually done before sowing to prevent the soil from becoming hard due to the gradual increase in sunlight and temperature.
Are farmers still using the plow?
In 1972, 85% of the land in the United States was cultivated with conventional tillage, and almost all of it was cultivated with the plow. However, by 2017, that percentage had dropped to just 28%. From 1972 to 2018, the amount of no-till land in the United States increased from 3.2 million acres to 109 million acres.










