Introduction
In agriculture, disc ploughs and disc harrows are common tillage tools that can enhance efficiency when preparing seedbeds. They are quite similar and both aid in soil cultivation, but do you know the differences between them? Clearly distinguishing them can help you use them better. Next, I will introduce them in terms of definition, usage, composition, and their impact on the land. Of course, I will also provide some tips for purchasing them.
Difference between disc plough and disc harrow
Definition
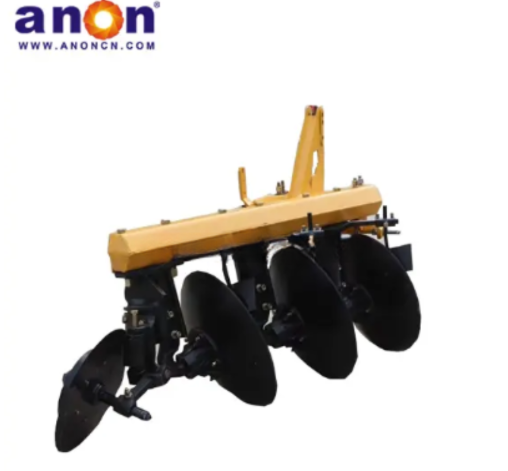
Disc Ploughs
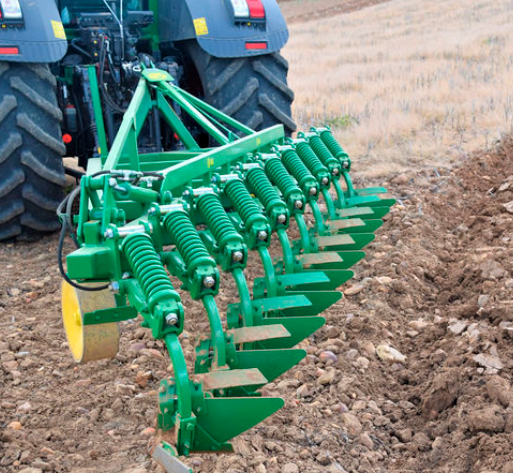
Disc ploughs are tillage machines with a disc plough body as their main working part. The disc is usually part of a hollow spherical surface, with its edge sharpened to facilitate cutting grass and penetrating into the soil. It does well in deep plowing and soil turning. Usually for the first step of land tillage. It typically consists of multiple large-diameter, concave steel plow discs. A standard disc plough generally has 3 to 6 disc ploughs. These plow discs, mounted on a frame and arranged at a certain angle, cut and turn the soil.

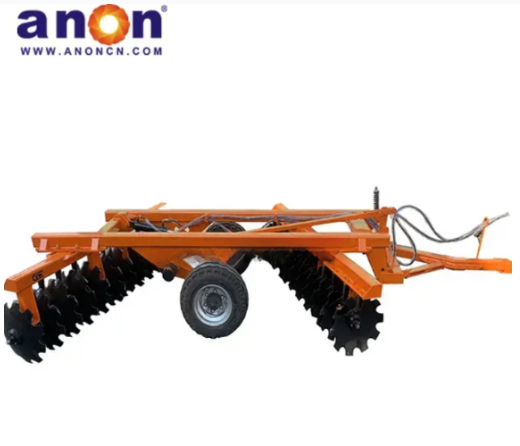
Disc Harrows
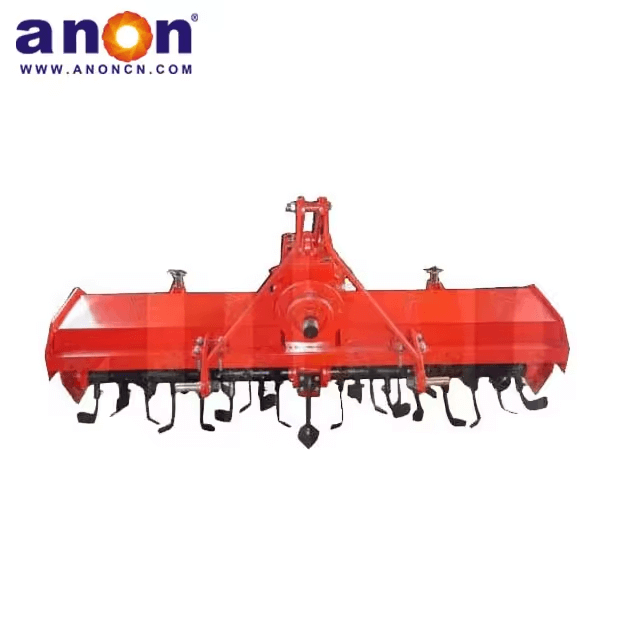
A disc harrow, with a group of concave discs fixed to a horizontal shaft as its working part, is a tillage tool used for secondary tillage after plowing. It has a strong soil penetration ability and can shatter soil clods and residue weeds, preparing the soil for planting. The disc harrow is usually equipped with a group of concave discs arranged in rows and also mounted on a frame. By adjusting the angle of the discs, it can achieve different depths of tillage and soil treatment.
Main Components
Disc Ploughs
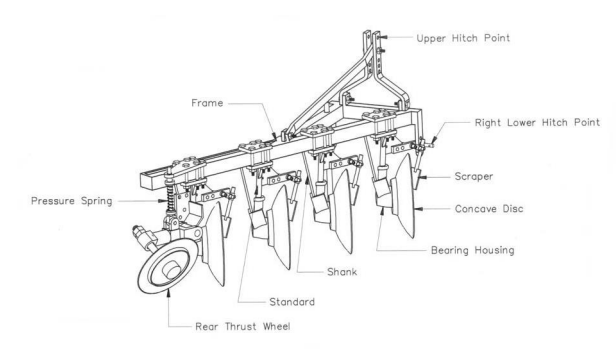
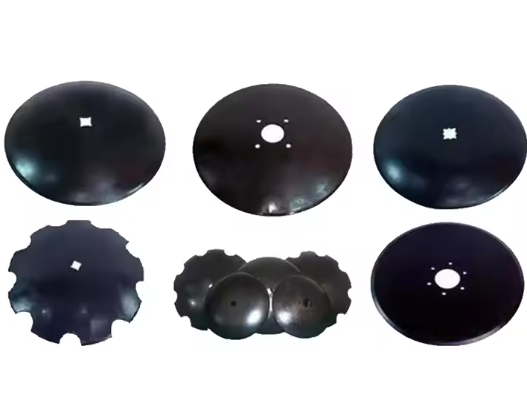
Discs
The concavity of the spherical surface of the disc plough is relatively large, and the thickness of its cutting edge typically ranges from 0.5 to 1 mm, making it sharp and suitable for deep tillage. It is responsible for cutting, turning, and loosening the soil. Additionally, the number, size, and angle of the plow discs will affect the tillage effectiveness.
Frame
The supporting structure of the framed disc plow bears tremendous pressure during operation.
Disc Axle
The plow disc shaft fixes the plow disc and drives its rotation. By adjusting the angle of the plow disc shaft, one can control the cutting depth and angle of the plow disc.
Hitching Mechanism
The three-point suspension system not only allows the disc plow to rise and tilt but also maintains its stability during the plowing process.
Scraper
It can promptly scrape off the clay adhering to the plow disc and turn over the soil.
Depth Control Wheel
It can maintain the tillage depth and stability of the disc plow during operation, while also preventing excessive tillage depth and machine overturning.
Disc Harrows
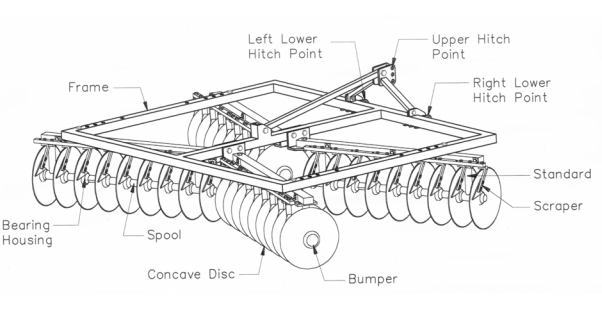
Disc Gangs
The characteristics of the disk harrow lie in its concave valve blade, with a smaller spherical concavity compared to the disk of a disk plow. It is used for superficial soil treatment, and adjusting the arrangement and angle of the disks can achieve different soil-cutting and mixing effects.
Frame
The harrow frame is the structure that supports the harrow assembly, maintaining the stability of the entire disk harrow.
Hitching Mechanism
It enables the disk harrow to lift, tilt, and maintain balance, ensuring that the disk harrow can be stably towed by a tractor for cultivation.
Towing Frame
When the disk harrow is connected in a towed manner, it is equipped with a towing frame, which also serves to ensure that the harrow can move freely in the field and perform cultivation.
Angle Adjustment Mechanism
It can help adjust the deflection angle of the disks to achieve different tillage depths.

Working Principle
Disc Ploughs
A disc plough uses concave discs to till the soil, and it is connected to the tractor in a three-point suspension manner during operation. When the disc plough is pulled forward by the tractor, the discs rotate around their central axes. The edges of the discs cut through the soil, and the soil lifted by the plow rises along the concave surface of the rotating discs and turns over to the side and rear. After tillage, furrows are left in the soil. As the soil rises along the concave surface of the discs, it is also cooperated with the scraper plate to turn and break up the soil clods.
Disc Harrows
During operation, the cutting edge plane of the disc harrow is perpendicular to the ground and forms an angle of deviation from the direction of travel. Each harrow group is supported by bearings on the frame. The disc harrow can be connected to the tractor in either a large traction or small traction manner. During operation, under the action of the tractor’s traction force and the soil’s reaction force, each harrow blade in the group rolls along with the square shaft as a whole. Due to the harrow’s own gravity, the cutting edge of the blade cuts into the soil, severing grass roots or crop residues, shattering the plowed soil clods, and causing the soil clods to rise slightly along the concave surface of the blade before falling over. This has a certain soil-turning and covering effect.
You can adjust the angle of deviation of the harrow group, typically within a range of 0° to 30°, with a common angle of deviation being 10° to 25°. Increasing the angle of deviation can enhance the blade’s penetration depth and improve soil-turning and soil-shattering effects, but it also increases resistance.
Main Functions
The primary function of a disc plow is deep tillage, breaking up compacted soil, covering crop residues, and burying green manure. Disc harrows are primarily used for breaking up soil, leveling plots, mixing crop residues and fertilizers, and shallow tillage, creating a loose, fine-textured surface seedbed for sowing.
Operation Stages
Disc plows are used for the first tillage, suitable for reclaimed land, land that has not been tilled for many years, with compacted soil, heavy clay soil, requiring deep burial of straw and weeds, or before planting deep-rooted crops.
Disc harrows are generally used for land preparation after plowing. Typically, after plowing, soil clods are turned over, allowed to dry, and then a tractor-pulled disc harrow is used to break up the clods, level the land, and loosen it shallowly, preparing seedbeds for sowing. This is suitable for small plots and light work.
Penetrating power
Disc Ploughs
The weight and robustness of the disc plough give it strong penetrating power. The large rotating disc blades can cut through and turn over the soil. With the weight of the plough and the force of the rotating discs, it is able to dig deep into the soil for deep tillage.

Disc Harrows
The disc harrow is generally not very heavy, usually weighing less than 80 kg, while the disc plow is heavier. Therefore, its penetrating power and strength are inferior to that of the disc plow. However, their main task is not to dig deep into the ground, but to work near the soil surface, such as preparing seedbeds. The disc harrow helps to level the soil and clear weeds after plowing.

Usage
Disc Ploughs
The disc plow is suitable for heavier soils such as clay, which require deep digging to break up compacted layers. It can effectively handle uncultivated land, turning over and breaking up hard, unworked soil or ground covered with weeds, thereby improving soil aeration and drainage. The main working part of the disc plow, the disc plow body, rolls forward with less friction resistance against the soil. It can also help cut weeds, featuring advantages such as being less prone to weed entanglement, clogging, and clay adherence. Additionally, the disc plow has long and wear-resistant cutting edges, making it easy to penetrate the soil. It is suitable for tillage operations in complex farmland with weedy growth, upright stems, high soil resistance, and soil containing brick fragments or other debris.
Disc Harrows
The disc harrow is suitable for various types of soil, especially for surface treatment of soil that has already undergone initial tillage. It can help you ensure there are no large clods and maintain a consistent tillage depth. It can also mix fertilizers and pesticides during tillage, effectively helping to disrupt the living environment of pests and cut weeds, creating favorable soil conditions for seeding, which is crucial for crop emergence and root growth. After harrowing, the soil surface is relatively flat and the soil is loose and crumbly. It demonstrates good adaptability even when working in areas with heavy clay soil, wasteland, and abundant weeds.
Working Depth
Disc Ploughs
The tilling depth of a disk plow is related to the diameter of its disks. Generally, the tilling depth of a disk plow is one-fourth to one-fifth of the disk diameter, allowing for efficient soil penetration and excavation.
Disc Harrows
The tilling depth of a disk harrow is usually related to its weight and the deflection angle of its blades. Increasing the counterweight of the disk harrow or enlarging the deflection angle can both enhance its soil penetration depth.
Soil Impact
Disc Ploughs
Disc ploughs are typically used for deep tillage, effectively breaking up the bottom layer of soil, and enhancing soil permeability and ventilation, which is beneficial for crop root growth and water infiltration. However, over-tillage can disrupt soil structure, increasing the risk of soil erosion.
Disc Harrows
Disc harrows are suitable for loosening shallow soil and leveling the ground to prepare the land for sowing crops. Proper use can effectively alter the soil surface structure, well-mix fertilizers, and cut weeds and stubs, increasing soil organic matter. However, you need to control the tilling depth to avoid the loss of topsoil.
Classification method
In addition to common classification methods such as suspension type, the presence of a drive shaft, and the availability of hydraulics, disk plows, and disk harrows also have their respective classification methods.
Disc Plough
Disc ploughs can be classified based on disk diameter, number, and the type of field they are used in, especially distinguishing between dryland plows, paddy field plows, and dual-purpose ploughs for both dry and paddy fields. Furthermore, there are ordinary types and vertical types according to their installation method. The rotating plane of an ordinary disc plough is not perpendicular to the ground but slightly inclined. In contrast, the rotating surface of a vertical disc plough is perpendicular to the ground, with only one deflection angle and no inclination.
Disc Harrow
Disk harrows can be classified based on their weight and structure. There are light-duty, medium-duty, and heavy-duty disk harrows based on weight. Categorized by structure, they include opposed, offset, folding, and double-row types.

Some Tips When Choosing the Equipment
When choosing between the two, there is usually no “best” option, but rather, it is the one that best suits your needs.
Soil Type
Firstly, when selecting a disk plow or disk harrow, consider the type of land, as soil hardness affects tillage effectiveness. For light or normal soil, choose a disk plow with a smaller diameter; for harder or heavier soil, opt for a larger diameter disk plow. Lightweight soil is easy to cultivate, so a lightweight disc rake is sufficient. For medium-hard soil, select a medium-duty disk harrow, and for sticky and hard soil, a heavy-duty disk harrow is necessary.
Tractor
Secondly, both the disc plow and the disc harrow need to be used with a tractor, so you need to consider the tractor’s horsepower, traction method and other conditions. If the tractor’s horsepower is insufficient, it cannot provide enough power for the disc plow or disc harrow, affecting its working efficiency. In addition, you also need to consider the tractor’s traction method and choose a disc plow and disc harrow that matches the tractor.
Hydraulic System
Then, both disc ploughs and disc harrows come in hydraulic and non-hydraulic versions. If you need to frequently adjust the direction of the disk plough or disk harrow, the hydraulic version will be more convenient for you.
Budget
Lastly, consider your budget. There are many manufacturers producing these two types of machines on the market. Having a good understanding of the prices offered by some manufacturers will help you obtain a cost-effective product through comparison. Of course, while focusing on price, you should also pay attention to the supplier’s qualifications and machine quality.
Wrap up
After comparing various aspects, I am sure you have understood the differences between them and realize that you can narrow down your choices based on certain factors to make a more suitable decision. If you still have any questions, feel free to consult us at ANON. As a reputable supplier, we will provide you with professional advice.
FAQ
How to maintain the disc rake?
You need to regularly check the condition of the parts. After ploughing with a disc rake, clean them promptly to prevent dirt accumulation. Additionally, apply lubricating oil to the frequently rubbed parts to minimize wear. If any parts show excessive wear or damage, replace them with original parts to ensure quality.











