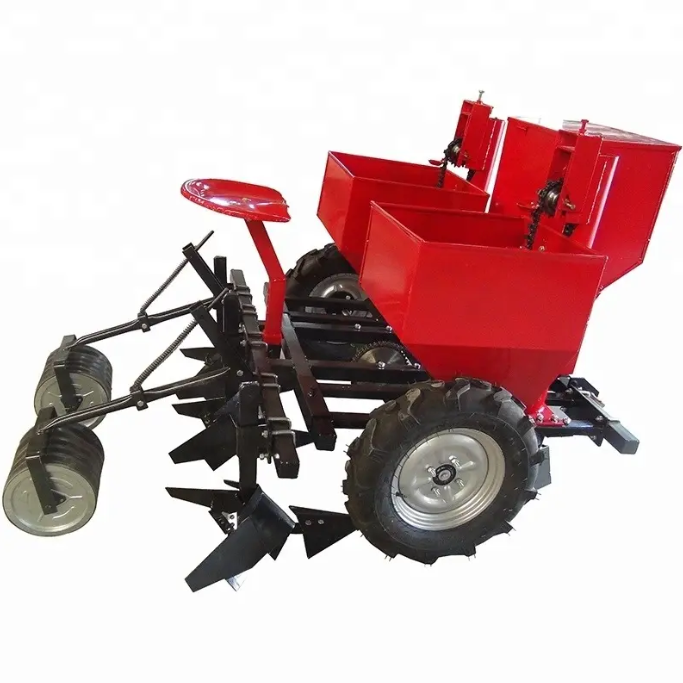
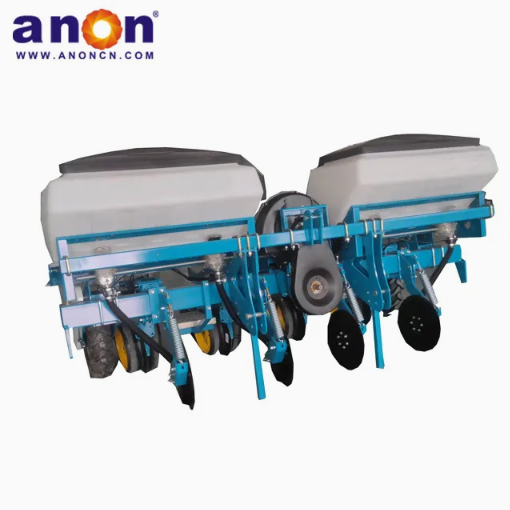
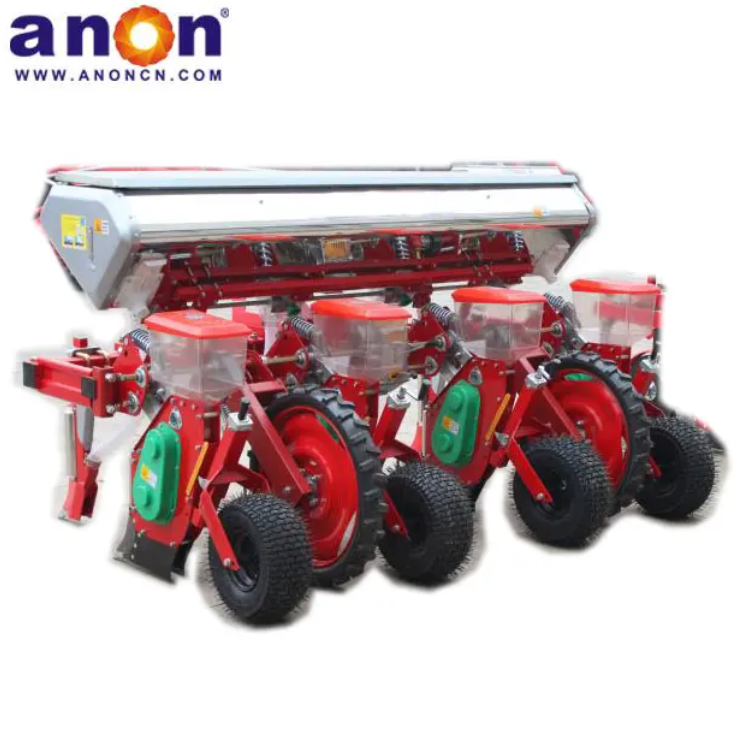
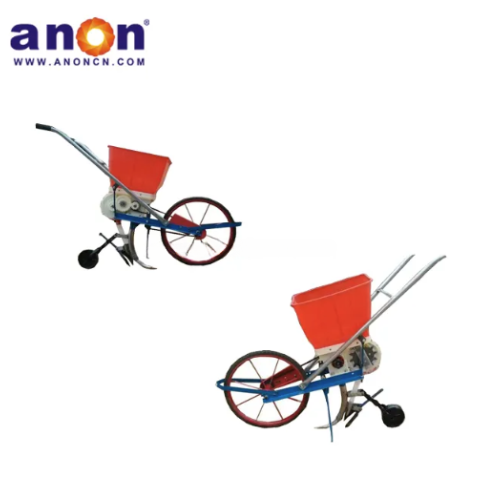
Potato Planter Machine
ANON potato seeder is a specialized agricultural equipment used for potato tuber sowing operations. The potato planter can complete the following tasks:
1. Ditch: Divide planting rows neatly by digging trenches with shovels.
2. Sowing: evenly pour the sweet potatoes into the ditch.
3. Covering soil: using a soil covering device to cover the soil.
4. Suppression or ridging (some models): promotes root development and increases seedling emergence rate.
Ditching, fertilizing, sowing, covering, and compacting are all completed in one go, bidding farewell to heavy manual labor. The daily sowing amount is as high as 18 acres.
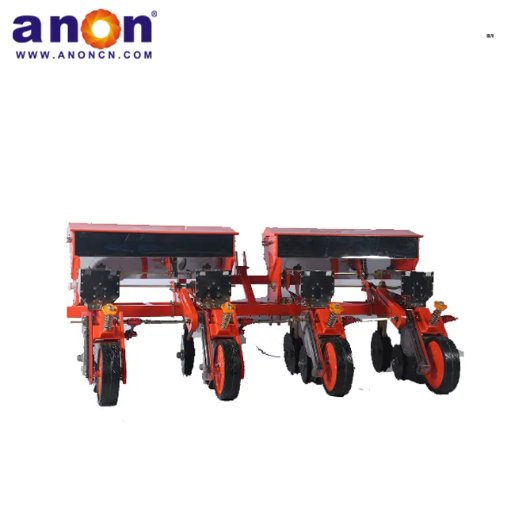
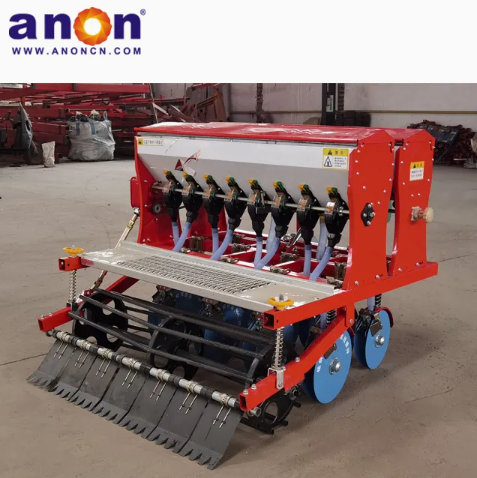
Our Products
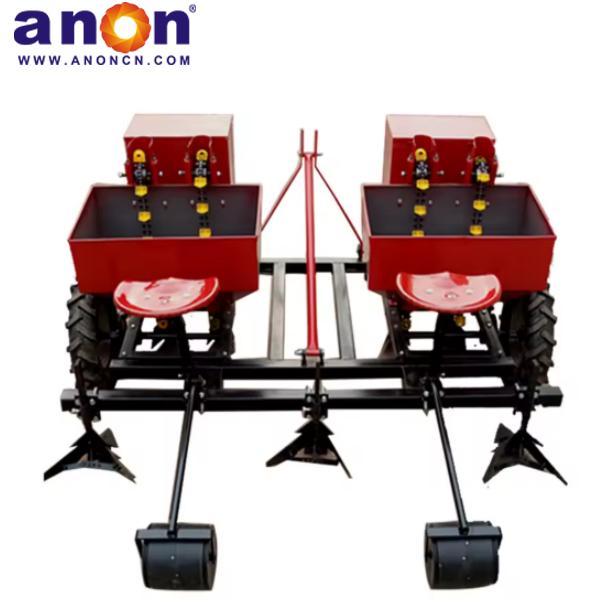
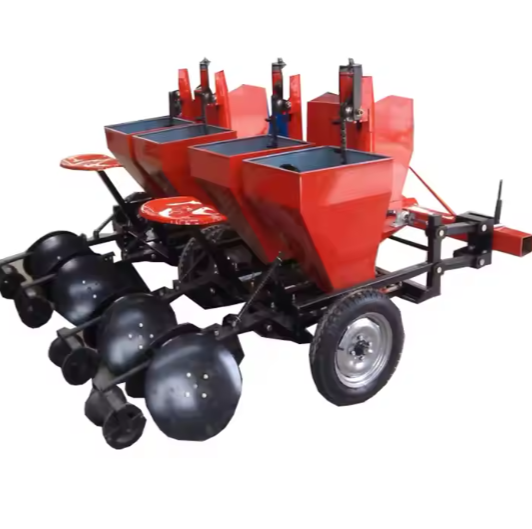
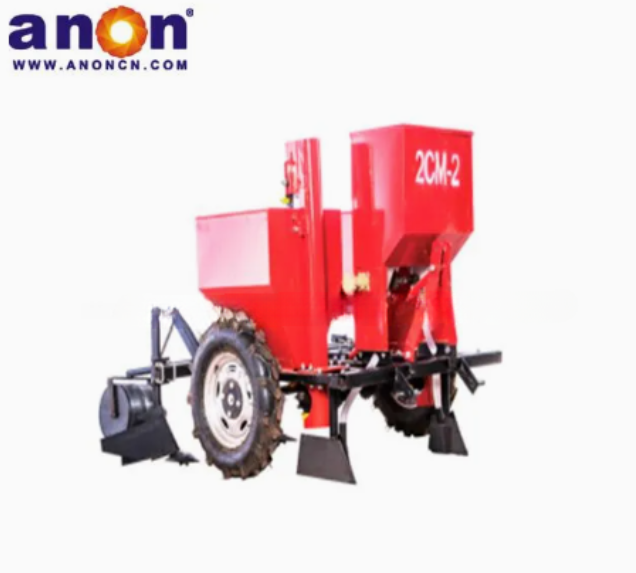
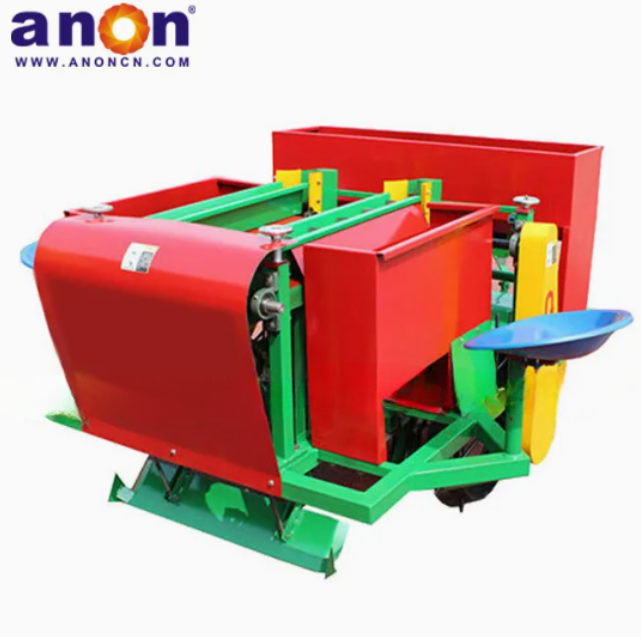
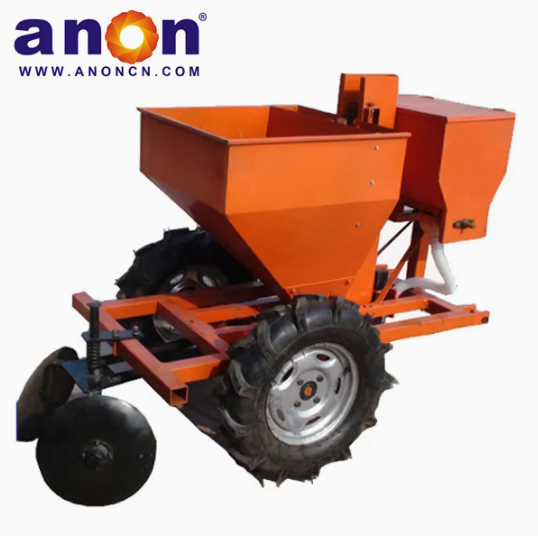









Higher Germination Rate
Our potato planter machine comes with a precision seeding system. The plant spacing, row spacing, and depth of our potato planter can be adjusted freely, with plant spacing of 20-40cm and row spacing of 22-28cm to meet the needs of different varieties. Accurate sowing can be achieved, increasing the germination rate by 30%. And we have a chain spoon or clip-type seeding device for you to choose from. The seeding spoon can adapt to potatoes of different sizes, accurately take seeds, eliminate missed seeding and reseeding, and ensure uniform and strong seedlings.
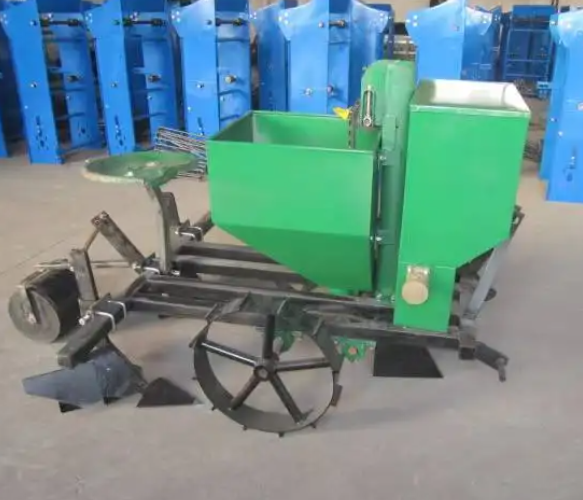

All-terrain Adaptability
Whether you’re working on vast plains, terraced hillsides, or small greenhouse plots. Our tractor’s three-point hitch system adapts to the terrain, handling slopes up to 15° with ease. It runs smoothly on sandy loam without slipping and won’t clog in sticky clay. Even freshly tilled fields are ready to plant—no need for a second pass. Save labor, save hassle!
Applications and operation Tips


FAQ
Potatoes prefer slightly acidic soil (pH 5.8-6.5). For best results, apply fertilizer or compost. If you want to make weeding easier (and you have enough space), plant the potatoes at least two feet apart to make weeding easier.
Planting deep. An important factor in growing large quantities of potatoes is planting deep. I dig a 12-inch deep trench and plant the seed potatoes at the bottom of the trench. I then cover with 4-6 inches of loose, well-drained soil rich in organic matter.
Avoid planting potatoes in soils with too much clay and waterlogging. Do not let the potato bed dry out. Check the soil moisture at least once a week throughout the summer. During dry spells, always water the potatoes using drip irrigation or soaker hoses.